Vehicle emissions have a significant impact on air quality and the environment, making emission control systems crucial in modern automobiles. Among these systems, the catalytic converter stands out as a critical component in reducing harmful pollutants. Whether you’re concerned about its function, maintenance, or even theft, understanding what a catalytic converter is and how a catalytic converter works is essential for vehicle owners.

What Is a Catalytic Converter?
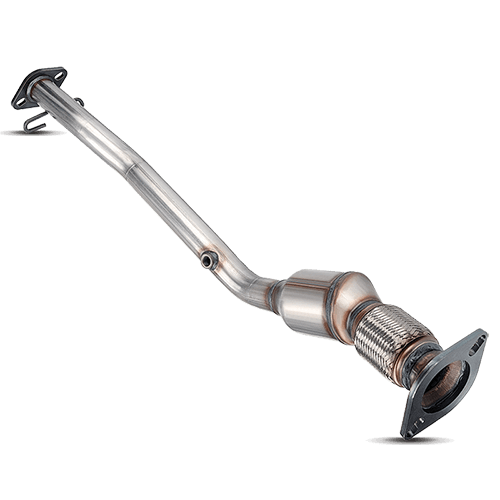
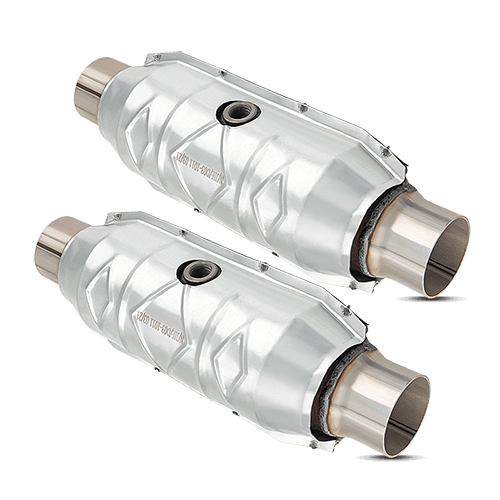
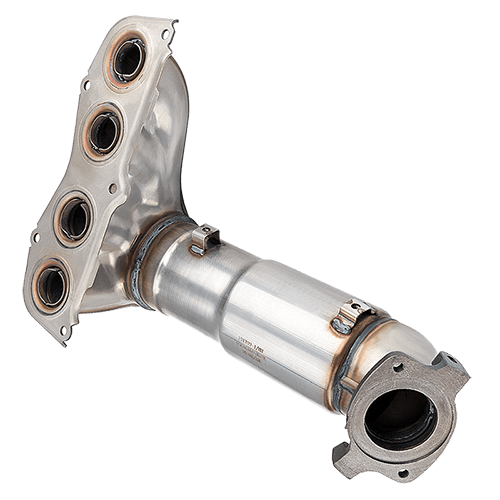
A catalytic converter is an important part of your car’s exhaust system that helps protect the environment. It looks like a small metal can and is installed in the exhaust pipe. Inside, it contains a special ceramic material coated with precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium.
Its main job? To clean up the harmful gases that come out of your engine.
When your engine runs, it produces three main types of pollutants:
Hydrocarbons (HC) – unburned fuel that contributes to smog,
Carbon monoxide (CO) – a poisonous gas,
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) – gases that can cause acid rain and harm your lungs.
The catalytic converter uses chemical reactions (oxidation and reduction) to turn these harmful gases into safer substances, like:
Water vapor (H₂O),
Carbon dioxide (CO₂),
And nitrogen gas (N₂).
Thanks to the catalytic converter, your vehicle produces cleaner exhaust and helps reduce air pollution.
Where Is the catalytic converter Located?
The catalytic converter is typically located near the front of the vehicle, close to the engine block. It has a box-like metal cylinder shape with two pipes - one connected to the engine and the other leading into the muffler. The exact location may vary depending on the make and model of your car, so it's best to consult your owner's manual or speak with a professional auto mechanic if you're unsure.
How many catalytic converters does a car have?
As for the number of catalytic converters, this can differ based on the vehicle specifications and local emissions requirements. Most cars have either one or two catalytic converters, but some high-performance models with larger engines may feature three to provide enhanced emission control capabilities.
How Does a Catalytic Converter Work?
As a key part of your car's exhaust system, the catalytic converter uses special materials—like platinum, palladium, and rhodium—to change dangerous gases into safer ones.
Here’s how it works:
Rhodium (Rh) helps turn nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are harmful to breathe, into nitrogen gas, which is safe.
Platinum (Pt) and Palladium (Pd) help convert carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), which are much less harmful.
The converter also uses rare earth elements, which help store and release oxygen. This improves the reaction and keeps the converter working well. These elements also:
Keep the coating stable,
Help with reactions involving water and gases,
And improve how fast and efficiently the chemical reactions happen.
Some of the key chemical reactions inside the converter are:
2CO + 2NO → 2CO₂ + N₂
2CO + O₂ → 2CO₂
2HC + O₂ → H₂O + 2CO₂
Temperature Matters
For a catalytic converter to work well, it needs to get hot—really hot. It usually starts working at around 260°C (500°F), but only at about 50% efficiency. Most converters fully "light off" (reach full power) between 480°C and 870°C (896°F to 1,598°F).
However, if the temperature gets too high (above 950°C or 1,742°F), it can damage the catalyst inside and reduce its lifespan.
So in short, your catalytic converter is like a high-heat filter, using chemistry and precious metals to turn harmful gases into safer ones—keeping both your car and the air cleaner.
Why Are Catalytic Converters Important?
Catalytic converter helps to significantly reduce the pollutants released from internal combustion engines, contributing to cleaner air and improved public health.
Catalytic converters are crucial for meeting strict emissions regulations. Governing bodies like the EPA set increasingly stringent standards that automakers must comply with to sell their vehicles. The effective performance of catalytic converters is heavily dependent on meeting these regulations.
Do Catalytic Converters Go Bad?
Yes, catalytic converters can indeed deteriorate over time. As an integral component of a vehicle's emissions system, the catalytic converter plays a crucial role in reducing pollutants in the exhaust fumes. However, as the converter ages, its ability to effectively convert these harmful substances diminishes, leading to decreased fuel efficiency and potentially poorer engine performance.
On average, catalytic converters have a lifespan of around 10 years. Nonetheless, various factors can cause them to fail prematurely, including age-related wear and tear, physical damage from extreme heat or road vibrations, and even the use of certain fuel additives or engine oils that can potentially compromise the converter's integrity.
Shop a New Catalytic Converter Today
At Philtop, we understand the importance of maintaining your vehicle's emissions control system. That's why we offer a comprehensive selection of high-quality catalytic converters at unbeatable prices, with the added convenience of free shipping to ensure timely delivery. Whether you require a direct-fit or universal-fit converter, our range has the perfect solution for your needs.
Crafted with only the most reliable materials and designed to meet or exceed OEM standards, our catalytic converters are built to provide years of efficient performance, even under heavy usage. And for added peace of mind, all our products come with a 90-day warranty against manufacturer defects, so you can have confidence in your purchase.
Learn more about Philtop Auto's catalytic converters. Click Here>>